In the digital era, businesses and organizations across various industries are increasingly embracing the digitization of documents. This shift from paper-based systems to digital document management offers numerous benefits, from improved efficiency and accessibility to enhanced security and cost savings. In this blog, we will explore the process of digitizing documents, the advantages it brings, and best practices for successful implementation.
What is Document Digitization?
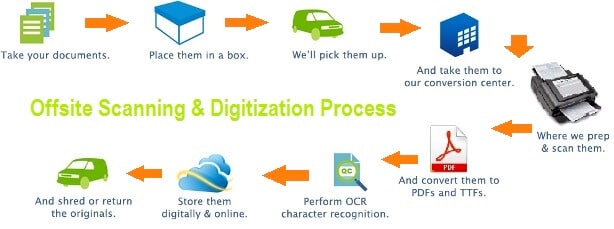
Document digitization is the process of converting physical paper documents into digital formats. This involves scanning, indexing, and storing documents electronically, making them easily accessible and searchable through digital devices. Digitization can be applied to a wide range of documents, including invoices, contracts, records, and more.
The Benefits of Document Digitization
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: Digitized documents can be accessed and shared instantly, eliminating the time-consuming process of searching through physical files. This leads to increased efficiency and productivity, as employees can quickly find the information they need and collaborate more effectively.
- Enhanced Accessibility: With digitized documents, employees can access important files from anywhere, at any time, using digital devices. This is especially beneficial for remote work and global teams, enabling seamless collaboration and ensuring that critical information is always within reach.
- Better Organization and Storage: Digital document management systems allow for better organization and categorization of files. Documents can be indexed and tagged with relevant keywords, making it easy to search and retrieve specific information. Additionally, digital storage reduces the need for physical storage space, freeing up valuable office real estate.
- Increased Security: Digitized documents can be encrypted and protected with access controls, ensuring that sensitive information remains secure. Digital backups also provide protection against physical damage or loss, such as from fires or floods, ensuring that important documents are preserved.
- Cost Savings: Digitizing documents can lead to significant cost savings by reducing expenses associated with paper, printing, and physical storage. Additionally, the time saved by quickly accessing and sharing digital documents translates into increased operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
The Digitization Process
- Document Preparation: Before digitization, documents need to be prepared by removing staples, paper clips, and any other binding materials. This ensures that the documents can be fed smoothly through the scanner.
- Scanning: Documents are scanned using high-quality scanners that capture images of the documents in digital formats, such as PDF or TIFF. Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology can be used to convert scanned images into searchable and editable text.
- Indexing: Scanned documents are indexed with relevant metadata, such as titles, dates, and keywords. This helps in organizing and categorizing the documents, making it easier to search and retrieve specific files.
- Quality Control: A quality control process ensures that all scanned documents are accurate and complete. Any errors or missing pages are identified and corrected to maintain the integrity of the digital files.
- Storage and Backup: Digitized documents are stored in a secure digital document management system. Regular backups are created to protect against data loss and ensure that documents can be recovered in case of any issues.
Best Practices for Document Digitization
- Plan and Prioritize: Develop a clear plan for digitizing documents, including identifying which documents to prioritize based on their importance and frequency of use. Start with high-impact documents that will provide immediate benefits to your organization.
- Choose the Right Tools: Invest in high-quality scanning equipment and document management software that meets your organization’s needs. Ensure that the tools you choose support OCR technology for searchable text and provide robust security features.
- Train Your Team: Provide training for your employees on the digitization process and the use of digital document management systems. Ensure that they understand the benefits of digitization and are equipped to use the new tools effectively.
- Maintain Consistency: Establish consistent naming conventions and indexing standards to ensure that digitized documents are organized and easily searchable. Consistency is key to maintaining an efficient digital document management system.
- Monitor and Improve: Regularly monitor the digitization process and gather feedback from your team to identify any areas for improvement. Continuously refine your processes to enhance efficiency and ensure the ongoing success of your digitization efforts.
Conclusion
The digitization of documents is a transformative step for businesses and organizations looking to improve efficiency, accessibility, and security. By converting physical documents into digital formats, organizations can streamline their operations, enhance collaboration, and reduce costs. Following best practices and leveraging the right tools can ensure a successful transition to digital document management, unlocking the full potential of digitization and driving long-term success in the digital age. Embrace the power of digitization and take your document management to the next level.
Title: Understanding the Difference Between OMR and OCR: A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of document processing and data extraction, two technologies frequently come into play: Optical Mark Recognition (OMR) and Optical Character Recognition (OCR). While both are used to automate data capture from physical documents, they serve distinct purposes and are suited for different types of data. In this blog, we will delve into the key differences between OMR and OCR, their applications, and how they can benefit various industries.
What is Optical Mark Recognition (OMR)?
Optical Mark Recognition (OMR) is a technology used to read and interpret marks on a document, such as checkboxes or bubbles. OMR systems are designed to detect the presence or absence of these marks, making it a highly efficient tool for processing forms and surveys where responses are captured using predefined mark patterns.
How OMR Works:
- Predefined Forms: OMR requires pre-designed forms with clearly defined areas for marking, such as bubbles or checkboxes.
- Scanning: The forms are scanned using OMR software or devices that capture the marks on the paper.
- Data Extraction: The software detects the presence or absence of marks within specified areas and translates this information into digital data.
Applications of OMR:
- Examinations and Tests: OMR is widely used in educational institutions for grading multiple-choice tests and exams.
- Surveys and Feedback Forms: OMR streamlines the processing of paper-based surveys and feedback forms, allowing for quick and accurate data collection.
- Attendance Tracking: OMR sheets are often used to record attendance in large-scale events or classrooms.
Advantages of OMR:
- Speed and Accuracy: OMR can process large volumes of forms quickly and accurately, minimizing human errors associated with manual data entry.
- Cost-Effective: OMR systems are relatively inexpensive to implement and maintain, making them ideal for organizations with high-volume form processing needs.
What is Optical Character Recognition (OCR)?
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is a technology that converts printed or handwritten text on scanned documents into machine-readable text. OCR is used to digitize text-based information, allowing for easy searching, editing, and storage of documents.
How OCR Works:
- Scanning: Documents are scanned using OCR software that captures the text on the paper.
- Character Recognition: The software analyzes the scanned images, recognizing and converting individual characters into digital text.
- Output: The converted text can be stored in various formats, such as PDF, Word, or plain text, making it searchable and editable.
Applications of OCR:
- Document Digitization: OCR is commonly used to digitize paper documents, such as contracts, invoices, and historical records, for easy access and archiving.
- Data Entry Automation: OCR automates the data entry process by extracting text from forms and documents, reducing the need for manual input.
- Text Recognition in Images: OCR is used to extract text from images, such as scanned books, magazines, and photographs.
Advantages of OCR:
- Enhanced Accessibility: OCR makes text-based information easily accessible and searchable, improving productivity and efficiency.
- Time Savings: OCR significantly reduces the time required for data entry and document processing.
- Data Preservation: OCR helps preserve important historical documents by converting them into digital formats for long-term storage and retrieval.
Key Differences Between OMR and OCR
|
Aspect |
OMR |
OCR |
|
Purpose |
Detects marks on predefined forms |
Recognizes and converts text from scanned images |
|
Input |
Marks (checkboxes, bubbles) |
Printed or handwritten text |
|
Applications |
Exams, surveys, attendance tracking |
Document digitization, data entry automation |
|
Technology |
Requires specific form design |
Analyzes text patterns in images |
|
Output |
Digital data indicating mark presence/absence |
Machine-readable text |
|
Flexibility |
Limited to predefined mark areas |
Flexible with various text layouts and fonts |
|
Error Handling |
Susceptible to errors if marks are not clear |
Advanced algorithms improve accuracy with text |
Choosing Between OMR and OCR
When deciding whether to use OMR or OCR, consider the nature of your documents and the type of data you need to extract:
- Use OMR if:
-
- You need to process forms with predefined marks, such as multiple-choice tests or surveys.
- Speed and accuracy in detecting mark presence are critical.
- Use OCR if:
-
- You need to digitize text-based documents for searching, editing, or archiving.
- You have a variety of document types and formats, including handwritten text.
Conclusion
OMR and OCR are powerful technologies that streamline data extraction from physical documents. While OMR excels in processing forms with predefined marks, OCR is the go-to solution for digitizing text-based documents. By understanding the key differences and applications of these technologies, businesses and organizations can make informed decisions to enhance their document processing workflows and improve overall efficiency. Whether you’re grading exams or digitizing archives, the right technology can make all the difference in managing your data effectively in the digital age.





Leave a Reply