Gabapentin is a widely prescribed medication used to manage various neurological and chronic pain conditions. Its versatility and effectiveness make it a popular choice for doctors and patients alike. However, finding the right dosage is crucial for optimal relief and minimal side effects. In this article, we delve into the specifics of Gabapentin 100mg and Gabapentin 400mg, comparing their uses, benefits, and considerations to help you make informed decisions about your treatment.
What is Gabapentin?
Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication originally developed to treat seizures. Over time, it has become a go-to treatment for neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, and even restless leg syndrome. By interacting with calcium channels in the nervous system, gabapentin helps to calm overactive nerve signals, reducing pain and discomfort.
Gabapentin 100mg is in a class of medications called anticonvulsants. Gabapentin 100mg treats seizures by decreasing abnormal excitement in the brain. Gabapentin 100mg relieves the pain of PHN by changing the way the body senses pain.
Key Uses of Gabapentin
-
Neuropathic Pain: Commonly prescribed for conditions like diabetic neuropathy or post-herpetic neuralgia.
-
Seizure Disorders: Effective as an adjunctive therapy for partial seizures.
-
Fibromyalgia: Provides relief from widespread muscle pain and fatigue.
-
Restless Leg Syndrome: Alleviates the urge to move legs due to discomfort.
Gabapentin 100mg: A Low-Dose Introduction
The 100mg dosage of gabapentin is often used as an introductory or maintenance dose. It’s particularly beneficial for individuals who are new to the medication or those who require minimal therapeutic effects.
Benefits of Gabapentin 100mg
-
Tolerability: Lower risk of side effects such as dizziness or drowsiness.
-
Gradual Onset: Allows the body to adapt to the medication without overwhelming the system.
-
Flexible Usage: Ideal for patients who may need to increase their dosage gradually.
Who Should Consider Gabapentin 100mg?
-
Patients with mild neuropathic pain.
-
Individuals starting gabapentin therapy.
-
Those sensitive to higher doses or prone to side effects.
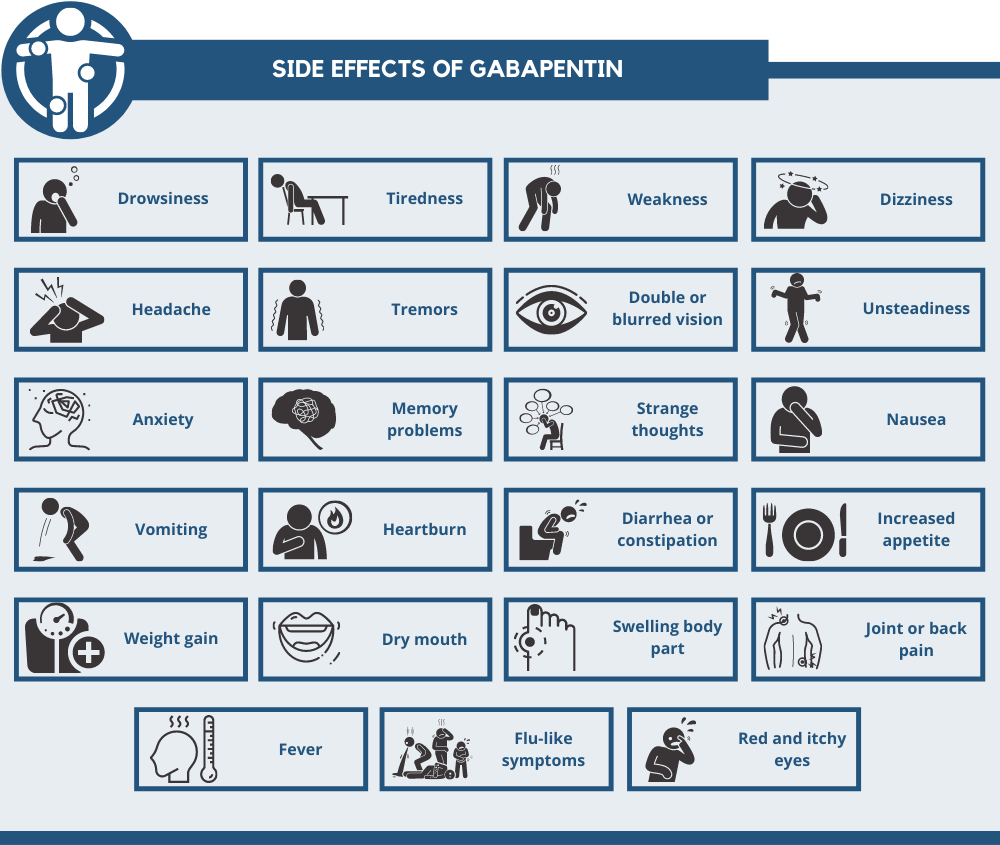
Potential Side Effects at 100mg
Even at low doses, gabapentin may cause:
-
Drowsiness
-
Fatigue
-
Nausea
-
Mild dizziness
Gabapentin 400mg: A Potent Option
The 400mg dosage of gabapentin is considered a more robust option for managing moderate to severe symptoms. It is typically prescribed when lower doses fail to provide adequate relief.
Gabapentin 400mg extended-release tablets (Horizant) treat restless legs syndrome (RLS), which causes discomfort in the legs and a strong urge to move them, especially at night and when sitting or lying down.
Advantages of Gabapentin 400mg
-
Enhanced Pain Relief: Suitable for chronic or intense neuropathic pain.
-
Fewer Increments Needed: Reduces the need for frequent dose adjustments.
-
Versatile Applications: Commonly used in conditions requiring higher therapeutic levels.
Who Benefits from Gabapentin 400mg?
-
Patients with severe neuropathic or chronic pain.
-
Individuals who have developed tolerance to lower doses.
-
Those managing conditions like post-herpetic neuralgia or refractory epilepsy.
Side Effects of Gabapentin 400mg
Higher doses may increase the likelihood of side effects, such as:
-
Dizziness
-
Coordination issues
-
Memory impairment
-
Swelling in extremities
Gabapentin Dosage Comparisons: 100mg vs. 400mg
Efficacy
-
100mg: Best for mild symptoms and gradual therapy initiation.
-
400mg: Provides robust relief for more intense pain or advanced conditions.
Side Effects
-
100mg: Minimal, often limited to mild drowsiness or nausea.
-
400mg: Higher chance of dizziness, fatigue, and coordination issues.
Cost and Accessibility
Both dosages are widely available, but costs may vary depending on insurance coverage and pharmacy location. Typically, higher doses may cost slightly more.
How to Choose the Right Dosage
Finding the appropriate gabapentin dosage depends on several factors:
-
The severity of Symptoms: Mild symptoms often respond well to 100mg, while severe pain may require 400mg or higher.
-
Patient Age and Weight: Dosage adjustments are often necessary for pediatric and elderly patients.
-
Tolerability: Those prone to side effects may need to start with lower doses and increase gradually.
-
Doctor’s Recommendations: Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized dosage guidance.
Tips for Safe Gabapentin Use
-
Follow Prescriptions Carefully: Never alter your dosage without consulting your doctor.
-
Monitor Side Effects: Report any adverse effects, especially if they worsen over time.
-
Avoid Abrupt Discontinuation: Gradually taper off gabapentin under medical supervision to prevent withdrawal symptoms.
-
Pair with Lifestyle Adjustments: Combining gabapentin with physical therapy, stress management, and a healthy diet can enhance results.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can I switch from 100mg to 400mg directly?
Switching between dosages should always be done gradually and under medical supervision to avoid side effects or complications.
How long does it take for gabapentin to work?
Gabapentin’s effects are typically noticeable within a few days, but full benefits may take up to two weeks of consistent use.
What if I miss a dose?
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it’s close to your next scheduled dose, skip the missed one and continue as normal. Avoid doubling up doses.
Can I take gabapentin with other medications?
Gabapentin can interact with certain drugs, including opioids and antacids. Always inform your doctor about any other medications you’re taking.
Conclusion
Choosing the right gabapentin dosage—whether 100mg or 400mg—is a critical step in effectively managing your condition. Both dosages offer unique benefits and are suited to different levels of symptom severity. By working closely with your healthcare provider and monitoring your body’s response, you can achieve optimal pain relief while minimizing side effects.





Leave a Reply