Introduction
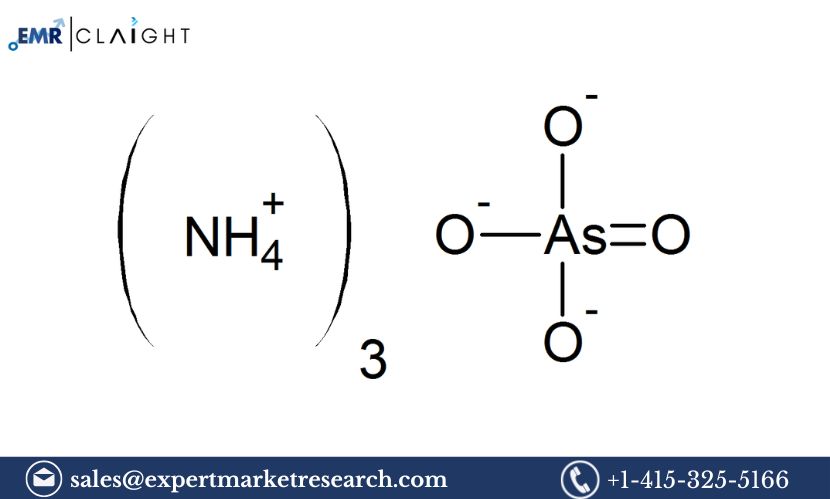
Ammonium arsenite, also known as arsenic triamide or ammonium arsenite, is a chemical compound with significant applications in various industries, including agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. It is primarily used as an intermediate in the production of other arsenic compounds, and in certain agricultural products as a pesticide. Due to its toxic and hazardous nature, it requires stringent safety measures during production and handling. Establishing an ammonium arsenite manufacturing plant can be a lucrative opportunity for businesses looking to tap into the global demand for chemicals used in industrial, agricultural, and research applications. This Ammonium Arsenite Manufacturing Plant Project Report provides an in-depth analysis of the process of setting up an ammonium arsenite manufacturing plant, including market analysis, plant design, manufacturing process, equipment requirements, financial considerations, and safety and environmental guidelines.
Market Overview and Demand
Ammonium arsenite is primarily used in the production of other arsenic-based chemicals, including arsenic acid, arsenic trichloride, and arsenic-based pesticides. The compound has diverse applications in different industries:
- Agriculture: Ammonium arsenite has been historically used as a pesticide and herbicide. While its use in agriculture has declined due to its toxic nature, it remains relevant in certain regions for pest control in crops like cotton and vegetables.
- Pharmaceuticals: The compound is used in the synthesis of certain arsenic-containing pharmaceuticals, including some treatments for diseases like leishmaniasis and malaria.
- Chemical Manufacturing: Ammonium arsenite serves as an intermediate in the production of other arsenic compounds, which are essential in various chemical processes, including electronics, glass manufacturing, and metal alloys.
- Research and Laboratories: Due to its chemical properties, ammonium arsenite is utilized in laboratories for various chemical reactions, including those involving arsenic in controlled environments.
Although ammonium arsenite is less commonly used today in some industries due to its toxicity, it remains a critical ingredient for producing several important chemicals and compounds. As industries continue to develop and innovate, the demand for ammonium arsenite in specialized applications, especially in emerging markets, is expected to grow.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Key Considerations for Setting Up an Ammonium Arsenite Manufacturing Plant
1. Location Selection
Selecting the right location for the ammonium arsenite manufacturing plant is crucial for operational efficiency, safety, and regulatory compliance. Key considerations include:
- Proximity to Raw Materials: The main raw materials for the production of ammonium arsenite are arsenic trioxide and ammonium hydroxide. Ensuring the location is near suppliers of these raw materials can help reduce transportation costs and improve supply chain reliability.
- Accessibility to Infrastructure: The plant should be located in an area with robust infrastructure, including good transportation networks, electricity, water supply, and waste management systems.
- Regulatory Compliance: The plant must adhere to local and international environmental, safety, and health regulations. Ammonium arsenite is toxic, so the location should comply with stringent environmental protection standards to manage waste and emissions.
- Labor Availability: Skilled labor, including chemists, chemical engineers, safety officers, and production staff, must be available in the vicinity to ensure smooth plant operations.
2. Plant Design and Layout
The design and layout of the plant must focus on efficiency, safety, and minimizing the environmental impact. The key areas to include in the plant layout are:
- Raw Material Receiving Area: This area should be designated for the safe receipt and inspection of raw materials, including arsenic trioxide and ammonium hydroxide. Appropriate storage and handling procedures should be implemented for these hazardous chemicals.
- Reaction Area: The reaction section is where ammonium arsenite is synthesized by reacting arsenic trioxide with ammonium hydroxide. This area should be equipped with reactors and temperature control systems.
- Filtration and Purification Area: After the reaction, the product mixture will need to be filtered and purified to remove any impurities. Filtration units and purification systems should be included in the plant layout.
- Drying and Packaging: The final product, ammonium arsenite, must be dried and then packaged in containers that ensure its safe storage and transportation.
- Waste Management Section: This area will manage the disposal of by-products and waste, including arsenic residues, which need to be handled with care due to their toxic nature.
3. Manufacturing Process
The production of ammonium arsenite typically involves the following steps:
-
Step 1: Raw Material Preparation: The primary raw materials, arsenic trioxide and ammonium hydroxide, are prepared in appropriate quantities. Arsenic trioxide is a white, crystalline powder, while ammonium hydroxide is a colorless liquid.
-
Step 2: Reaction: In the reactor, arsenic trioxide is mixed with ammonium hydroxide under controlled temperature and pressure conditions.
-
Step 3: Filtration and Separation: After the reaction, the mixture contains both the desired ammonium arsenite and by-products, including unreacted materials. The solution is filtered to remove any impurities.
-
Step 4: Drying: The filtered ammonium arsenite is then dried to remove excess moisture. Drying can be achieved using rotary dryers, tray dryers, or fluidized bed dryers, depending on the plant’s capacity and design.
-
Step 5: Packaging: The dried ammonium arsenite is then packaged into air-tight containers. Packaging can be done in bags, drums, or sealed bottles to prevent moisture and contamination.
Key Equipment Required:
- Reactor: A chemical reactor for mixing arsenic trioxide and ammonium hydroxide under controlled conditions.
- Filtration Units: Used for separating unwanted by-products and unreacted materials from the ammonium arsenite solution.
- Dryers: Rotary or fluidized bed dryers to remove moisture from the final product.
- Packaging Equipment: Automated or manual equipment for packing the final product into suitable containers.
4. Raw Materials and Supply Chain Management
The primary raw materials for the production of ammonium arsenite are:
- Arsenic Trioxide: This is the main source of arsenic for the production of ammonium arsenite. It is typically obtained through the processing of arsenic-containing ores or as a by-product in the refining of non-ferrous metals.
- Ammonium Hydroxide: This chemical compound is commonly available from chemical suppliers and is used to provide the necessary ammonium ions for the synthesis of ammonium arsenite.
A reliable supply chain for these raw materials is crucial for ensuring smooth operations and avoiding production delays. Establishing long-term contracts with suppliers of high-quality raw materials and ensuring proper storage conditions will help mitigate risks related to raw material shortages or contamination.
5. Quality Control and Testing
To ensure that ammonium arsenite meets the required quality standards, regular testing and quality control measures should be implemented:
- Purity Testing: The final product should be tested for purity to ensure that it contains the appropriate concentration of ammonium arsenite and does not contain harmful impurities.
- Particle Size Distribution: The particle size of ammonium arsenite powder should be monitored to ensure that it is suitable for its intended applications, particularly in agriculture and pharmaceuticals.
- Toxicity Testing: Given the toxic nature of ammonium arsenite, its safety for handling and transportation should be assessed. The compound should be tested for any potential hazards during manufacturing and handling.
6. Environmental and Safety Considerations
Ammonium arsenite is a highly toxic and hazardous substance. Therefore, strict safety measures must be in place to ensure the protection of workers, the environment, and the surrounding community. Key safety considerations include:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Workers should be equipped with appropriate PPE, including gloves, goggles, and respiratory protection, to minimize exposure to toxic chemicals.
- Ventilation Systems: The plant should be equipped with efficient ventilation systems to remove harmful vapors and gases, particularly in the reaction and drying areas.
- Waste Disposal: Any waste generated during production, including arsenic residues, should be properly disposed of in compliance with local environmental regulations. The plant should have a waste treatment system to neutralize toxic by-products before disposal.
- Emergency Response Plan: An emergency response plan should be developed and regularly updated. This includes procedures for handling chemical spills, fires, or accidents.
7. Financial Planning and Investment
Setting up an ammonium arsenite manufacturing plant requires significant capital investment. A detailed financial analysis is essential to assess the feasibility and profitability of the project. Key financial components include:
- Initial Capital Investment: This includes the cost of land, plant construction, machinery, raw materials, and working capital.
- Operating Costs: Ongoing expenses such as raw material procurement, labor costs, energy consumption, and maintenance should be estimated.
- Revenue Projections: Revenue projections should be based on the expected demand for ammonium arsenite in various industries. Pricing strategies should consider both production costs and market demand.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Calculating the ROI will help determine the financial viability of the plant and its potential for generating profits in the long run.
8. Marketing and Distribution Strategy
To succeed in the competitive market for ammonium arsenite, a strong marketing and distribution strategy is essential:
- Target Markets: Identify key sectors such as agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing as the primary customers for ammonium arsenite.
- Branding: Position the ammonium arsenite product as a high-quality, reliable chemical compound that meets industry standards for safety and efficacy.
- Distribution Channels: Build partnerships with chemical distributors, wholesalers, and direct customers to expand market reach. A strong online presence and sales network can also help in reaching potential customers.
Media Contact
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au





Leave a Reply