Polymer Matrix Composites (PMC) are advanced materials widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, construction, and sports equipment due to their superior strength, lightweight properties, and durability. The growing demand for high-performance materials has led to the rise of PMC manufacturing plants, which play a crucial role in producing these composites for various applications. Setting up a PMC manufacturing plant requires a deep understanding of materials science, manufacturing processes, and regulatory requirements. This article delves into the essential aspects of establishing a Polymer Matrix Composites manufacturing plant project, including key processes, considerations, and market opportunities.
What Are Polymer Matrix Composites (PMC)?
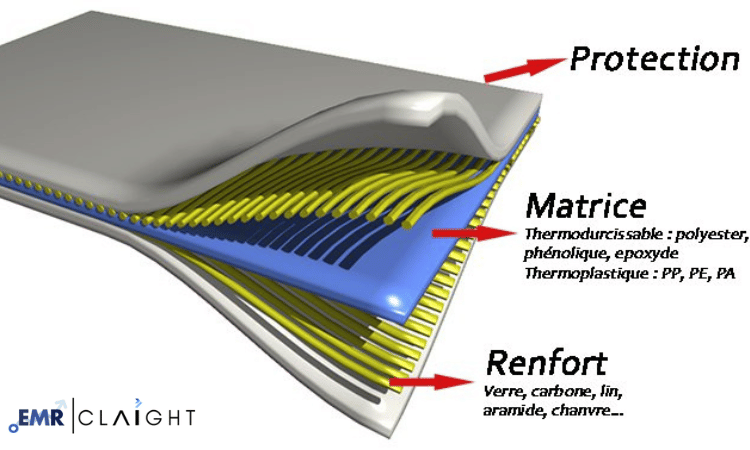
Polymer Matrix Composites (PMC) are materials made by combining a polymer resin with reinforcing fibers or particles to enhance their mechanical properties. The polymer acts as the matrix, holding the reinforcing material in place, while the fibers provide strength, rigidity, and impact resistance. This combination results in a material that is stronger, lighter, and more versatile than traditional materials, making it ideal for demanding applications.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@ https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/prefeasibility-reports/polymer-matrix-composites-pmc-manufacturing-plant-project-report/requestsample
Key Components of PMC:
- Polymer Matrix: This is the binder or matrix that holds the composite together. Common polymers used include epoxy, polyester, and vinyl ester resins.
- Reinforcing Material: Typically made from fibers such as carbon, glass, or aramid, these materials provide structural strength.
- Additives: To improve performance, additives like fire retardants, fillers, or tougheners may be included in the composite.
Applications of Polymer Matrix Composites
PMC materials are used in a wide range of industries where high performance and lightweight materials are required. Some of the most prominent applications include:
-
Aerospace and Aviation
The aerospace industry relies on PMC for the production of lightweight, high-strength components such as wings, fuselage parts, and engine components. The reduced weight of PMC helps improve fuel efficiency and performance. -
Automotive Industry
PMCs are used to manufacture various car parts, including body panels, bumpers, and interior components, offering a combination of light weight and high durability. They also help in meeting fuel efficiency standards. -
Construction and Infrastructure
PMCs are used in the construction of bridges, building facades, and reinforcement of structures. Their resistance to corrosion and high strength-to-weight ratio make them ideal for these applications. -
Sporting Goods
From bicycles to skis and tennis rackets, PMCs are increasingly used in the sports equipment industry. The materials provide enhanced performance while maintaining durability. -
Marine Industry
PMCs are utilized in the manufacture of boat hulls, deck structures, and marine equipment. The composites’ resistance to corrosion makes them highly valuable in this environment.
Steps in Setting Up a Polymer Matrix Composites Manufacturing Plant
1. Market Research and Feasibility Study
Before establishing a PMC manufacturing plant, conducting thorough market research is essential. Understand the demand for PMCs in various sectors, potential clients, competitors, and regional market conditions. A feasibility study will help determine the economic viability of the project, considering factors such as market demand, production costs, and return on investment.
2. Location Selection
Choosing the right location is crucial for the success of the manufacturing plant. Factors to consider include proximity to suppliers of raw materials, transportation networks, skilled labor, and regulatory environments. A location close to key markets or industrial hubs can reduce shipping costs and improve customer service.
3. Facility Design and Plant Layout
The design of the manufacturing facility should allow for efficient material flow, safety, and scalability. The plant should include areas for resin preparation, fiber handling, composite molding, curing, and finishing. It should also have a dedicated space for quality control and research and development (R&D).
4. Raw Materials Procurement
Procure high-quality raw materials such as polymers, fibers, and additives. Establish reliable relationships with suppliers to ensure the consistent supply of these materials. Sourcing high-quality fibers (like carbon or glass) and resins is essential for maintaining the integrity and performance of the final composite products.
5. Manufacturing Process and Equipment
PMC manufacturing involves several processes depending on the type of composite being produced. These include:
- Hand Lay-Up Process: A manual process where layers of fiber are applied to a mold, followed by resin infusion.
- Compression Molding: This process uses heat and pressure to shape the composite material.
- Filament Winding: A method used for creating cylindrical parts like pipes and tanks by winding fibers around a mold.
- Resin Transfer Molding (RTM): A closed molding process in which resin is injected into a fiber preform under pressure.
Investing in advanced machinery and automation can improve production efficiency and consistency.
6. Quality Control and Testing
Quality control is a critical part of PMC manufacturing. Testing is required to ensure the composites meet required strength, durability, and other performance standards. Non-destructive testing methods, such as ultrasonic testing or X-ray inspection, are often used to assess the integrity of the composites.
A robust quality assurance system should be implemented to monitor every stage of the manufacturing process, from raw material procurement to finished product testing.
7. Regulatory Compliance and Certification
PMCs, particularly those used in aerospace and automotive applications, must adhere to strict regulatory standards. This includes obtaining necessary certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and specific industry certifications. The plant must also comply with environmental regulations regarding waste disposal, emissions, and energy use.
Challenges in Polymer Matrix Composites Manufacturing
1. Cost of Raw Materials
The cost of high-quality fibers like carbon or aramid can be significant, impacting the overall cost of production. Fluctuations in raw material prices can make it challenging to maintain consistent production costs.
2. Technical Complexity
PMC manufacturing involves complex processes, and maintaining consistency in product quality requires high technical expertise. Issues such as fiber misalignment, improper resin mixing, or curing inconsistencies can affect the final product.
3. Skilled Workforce
The manufacturing of PMCs requires specialized knowledge and expertise in materials science and composite processes. Recruiting and training a skilled workforce is essential to ensure that production is efficient and that the products meet the required standards.
4. Environmental Impact
While PMCs offer environmental benefits, such as reduced vehicle weight for better fuel efficiency, the production process can generate waste and emissions. Ensuring sustainable practices in material sourcing, waste management, and energy use is vital for meeting environmental regulations.
Opportunities in the Polymer Matrix Composites Market
1. Growing Demand for Lightweight Materials
As industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction continue to focus on reducing weight for improved fuel efficiency and performance, the demand for PMCs is set to rise. Advances in manufacturing technologies and new applications are expected to further fuel this demand.
2. Innovation in Composite Materials
Continuous research into improving the properties of PMCs—such as making them more sustainable or cost-effective—provides opportunities for new product development. Companies can differentiate themselves by offering unique composite solutions tailored to specific industries.
3. Emerging Markets
Countries in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East are seeing rapid industrial growth, particularly in the automotive and infrastructure sectors. These regions present untapped potential for PMC manufacturers.
4. Recycling and Sustainability
With increasing focus on sustainability, opportunities exist for developing recycled composite materials and improving the energy efficiency of the manufacturing process. This not only benefits the environment but also appeals to eco-conscious customers.
Marketing and Distribution Strategies
To succeed in the competitive PMC market, companies need to implement effective marketing and distribution strategies:
- Partnerships with OEMs: Forming partnerships with original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) in sectors such as automotive and aerospace can help secure long-term contracts.
- Trade Shows and Exhibitions: Participating in industry events helps to build brand awareness and attract potential clients.
- Digital Marketing: An effective digital marketing strategy can help reach global clients and showcase the company’s expertise in PMC production.





Leave a Reply