Muscle relaxants are medications doctors often prescribe to treat muscle spasms, pain, and stiffness. These drugs work by targeting the central nervous system or directly affecting the muscles. They help reduce discomfort and improve mobility. Let’s explore the most commonly prescribed muscle relaxants, how they work, and their potential side effects.
What Are Muscle Relaxants?
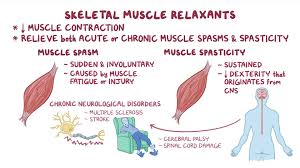
Muscle relaxants are drugs designed to relieve muscle spasms and pain. They are often prescribed for conditions like back pain, neck pain, or injuries. These medications can be divided into two main categories: antispasmodics and antispastics. Antispasmodics treat sudden muscle spasms, while antispastics help with muscle stiffness caused by conditions like multiple sclerosis or cerebral palsy.
How Do Muscle Relaxants Work?
Muscle relaxants work in different ways depending on their type. Some act on the brain and spinal cord to reduce muscle tension. Others block nerve signals in the muscles, preventing spasms. By targeting the nervous system or muscles directly, these drugs help ease pain and improve movement.
Commonly Prescribed Muscle Relaxants
Here are some of the most frequently prescribed muscle relaxants:
1. Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril)
Cyclobenzaprine is a popular muscle relaxant used for short-term relief of muscle spasms. It works by blocking nerve impulses that cause pain. Doctors often prescribe it for back or neck pain. Common side effects include drowsiness, dry mouth, and dizziness.
2. Methocarbamol (Robaxin)
Methocarbamol helps relieve muscle pain and stiffness. It works by depressing the central nervous system. This medication is often used for injuries or muscle strains. Side effects may include nausea, headache, and blurred vision.
3. Baclofen (Lioresal)
Baclofen is commonly prescribed for muscle stiffness caused by conditions like multiple sclerosis or spinal cord injuries. It works by relaxing the muscles and reducing spasms. Side effects can include weakness, fatigue, and confusion.
4. Tizanidine (Zanaflex)
Tizanidine is used to treat muscle spasms caused by conditions like multiple sclerosis or spinal cord injuries. It works by blocking nerve signals that cause muscle tightness. Common side effects include dry mouth, dizziness, and low blood pressure.
5. Carisoprodol (Soma)
Carisoprodol is a muscle relaxant that works by blocking pain sensations between the nerves and the brain. It is often prescribed for short-term relief of muscle pain. Side effects may include drowsiness, dizziness, and headache.
6. Metaxalone (Skelaxin)
Metaxalone is used to treat muscle pain and discomfort. It works by affecting the central nervous system to relax muscles. Side effects can include nausea, vomiting, and drowsiness.
Benefits of Muscle Relaxants
Muscle relaxants provide several benefits for patients with muscle pain or spasms. They help reduce pain, improve mobility, and enhance quality of life. These medications are particularly useful for short-term relief of acute muscle conditions. They can also be part of a broader treatment plan that includes physical therapy and exercise.
Potential Side Effects
While muscle relaxants are effective, they can cause side effects. Common side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, and dry mouth. Some people may experience more serious side effects like allergic reactions, liver damage, or dependence. It’s important to follow the doctor’s instructions and report any unusual symptoms.
Who Should Avoid Muscle Relaxants?
Muscle relaxants may not be suitable for everyone. People with certain medical conditions, such as liver disease or glaucoma, should avoid these medications. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their doctor before taking muscle relaxants. Older adults may be more sensitive to the side effects and should use these drugs with caution.
How to Use Muscle Relaxants Safely
To use muscle relaxants safely, follow these tips:
-
Take the medication exactly as prescribed.
-
Avoid alcohol while taking muscle relaxants.
-
Do not drive or operate heavy machinery if you feel drowsy.
-
Inform your doctor about all other medications you are taking.
-
Report any side effects to your doctor immediately.
Alternatives to Muscle Relaxants
For those who cannot take muscle relaxants or prefer non-drug options, there are alternatives. Physical therapy, stretching exercises, and heat or ice therapy can help relieve muscle pain. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen may also be effective. In some cases, alternative treatments like acupuncture or massage therapy can provide relief.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience severe muscle pain or spasms that do not improve with rest or over-the-counter treatments, see a doctor. Persistent pain could be a sign of a more serious condition. A healthcare professional can diagnose the problem and recommend the best treatment plan.
Conclusion
Muscle relaxants are valuable tools for managing muscle pain and spasms. They work by targeting the nervous system or muscles to reduce discomfort. While effective, these medications can cause side effects and may not be suitable for everyone. Always consult a doctor before starting any new medication. By understanding how muscle relaxants work and using them safely, you can find relief from muscle pain and improve your quality of life.





Leave a Reply