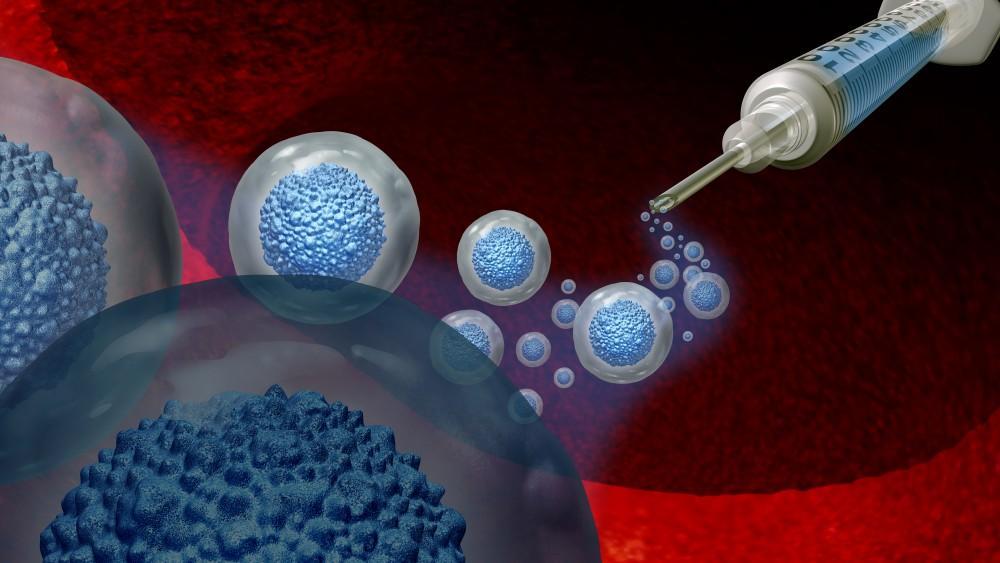
Regenerative medicine is revolutionizing the field of healthcare by focusing on repairing or replacing damaged tissues and organs. Through innovative techniques, regenerative medicine harnesses the body’s natural healing processes to restore function and improve overall health. From stem cell therapy to tissue engineering, this emerging area of medical science offers hope for patients suffering from a wide range of chronic conditions, injuries, and Rdegenerative diseases. In this article, we will explore the power of Regenerative medicine(الطب التجديدي) and its potential to transform modern healthcare.
What is Regenerative Medicine?
Regenerative medicine refers to medical treatments that aim to repair or replace damaged cells, tissues, or organs to restore function. Unlike traditional treatments that focus on managing symptoms, regenerative medicine targets the underlying causes of diseases or injuries. Key components of regenerative medicine include:
- Stem cell therapy: The use of stem cells to regenerate damaged tissues or organs.
- Tissue engineering: Creating new tissues or organs in the lab for transplantation.
- Gene therapy: Modifying genes to correct defects or improve the body’s ability to heal itself.
These cutting-edge techniques are still evolving, but their potential to transform medicine is immense, offering treatments for conditions that were once considered untreatable.
Stem Cell Therapy: The Cornerstone of Regenerative Medicine
Stem cell therapy is perhaps the most well-known application of regenerative medicine. Stem cells have the unique ability to develop into different types of cells, such as muscle, bone, or nerve cells, making them invaluable in the repair of damaged tissues. Stem cell therapy has shown promise in treating conditions such as:
- Osteoarthritis: Stem cells can help regenerate cartilage in joints, reducing pain and improving mobility.
- Spinal cord injuries: Stem cell injections may promote nerve regeneration and improve motor function.
- Heart disease: Stem cells can help repair heart tissue damaged by heart attacks, improving heart function.
Despite its potential, stem cell therapy is still being researched, and clinical trials are ongoing to better understand its efficacy and long-term safety.
Tissue Engineering: Creating Organs in the Lab
Tissue engineering is an exciting field within regenerative medicine that involves growing new tissues or even entire organs in the laboratory for transplantation. Researchers are developing techniques to create functional organs by combining stem cells with scaffolds that provide structural support. The potential benefits of tissue engineering include:
- Organ transplantation: Growing organs like kidneys or livers in the lab to meet the growing demand for donor organs.
- Custom-made tissues: Creating tissue types tailored to individual patients, reducing the risk of rejection.
- Regeneration of damaged tissues: Growing new tissues to repair damaged areas, such as skin or muscle.
While we are still a long way from mass-producing functional organs, advancements in tissue engineering have made significant strides in the last few years, offering new hope for patients in need of organ transplants.
Gene Therapy: Unlocking the Body’s Healing Potential
Gene therapy is another powerful tool in regenerative medicine. This technique involves modifying a patient’s genes to either replace defective genes or enhance the body’s ability to repair itself. Gene therapy can help treat a variety of conditions, including:
- Genetic disorders: Replacing defective genes that cause diseases like cystic fibrosis or sickle cell anemia.
- Cancer treatment: Using gene therapy to target cancer cells and boost the body’s immune response against tumors.
- Tissue regeneration: Introducing genes that promote tissue healing and regeneration, such as those that encourage the growth of new blood vessels or nerve cells.
Gene therapy holds enormous promise, but it also comes with challenges. Issues such as gene delivery methods, safety, and long-term effects must be addressed before widespread clinical use becomes feasible.
The Role of Regenerative Medicine in Treating Chronic Diseases:
One of the most exciting aspects of regenerative medicine is its potential to treat chronic diseases that are currently difficult to manage with conventional methods. Conditions like diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease may benefit from regenerative therapies aimed at repairing or replacing damaged cells or tissues. Examples of regenerative treatments for chronic diseases include:
- Diabetes: Regenerating insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas to restore normal blood sugar levels.
- Alzheimer’s disease: Replacing damaged neurons and improving brain function to slow or halt cognitive decline.
- Parkinson’s disease: Using stem cells to replace lost dopamine-producing neurons, potentially alleviating symptoms like tremors and rigidity.
While many of these treatments are still in experimental stages, they offer hope for patients who currently have few options beyond symptom management.
The Future of Regenerative Medicine: Challenges and Opportunities
The future of regenerative medicine is incredibly promising, but there are still challenges to overcome. The field requires significant research and development to ensure that treatments are both effective and safe. Some of the key challenges include:
- Ethical concerns: Issues surrounding stem cell sourcing and the use of gene editing technologies.
- Regulatory hurdles: The need for rigorous testing and approval processes to ensure the safety of new therapies.
- Cost and accessibility: The high costs of regenerative treatments may limit their availability to certain populations.
Despite these challenges, the future of regenerative medicine holds immense potential to revolutionize the way we treat diseases, injuries, and aging-related conditions. With continued advancements in technology and clinical research, regenerative medicine may soon become a mainstream solution for many patients worldwide.
Conclusion:
Regenerative medicine is an exciting and rapidly advancing field that has the potential to change the landscape of modern healthcare. From stem cell therapy and tissue engineering to gene therapy, the possibilities for treating chronic diseases, repairing damaged tissues, and even growing organs are vast. While there are still hurdles to overcome, the progress being made in regenerative medicine offers hope for millions of patients around the world. As research continues and treatments become more widely available, regenerative medicine may soon be at the forefront of healing the body in ways we never thought possible.





Leave a Reply