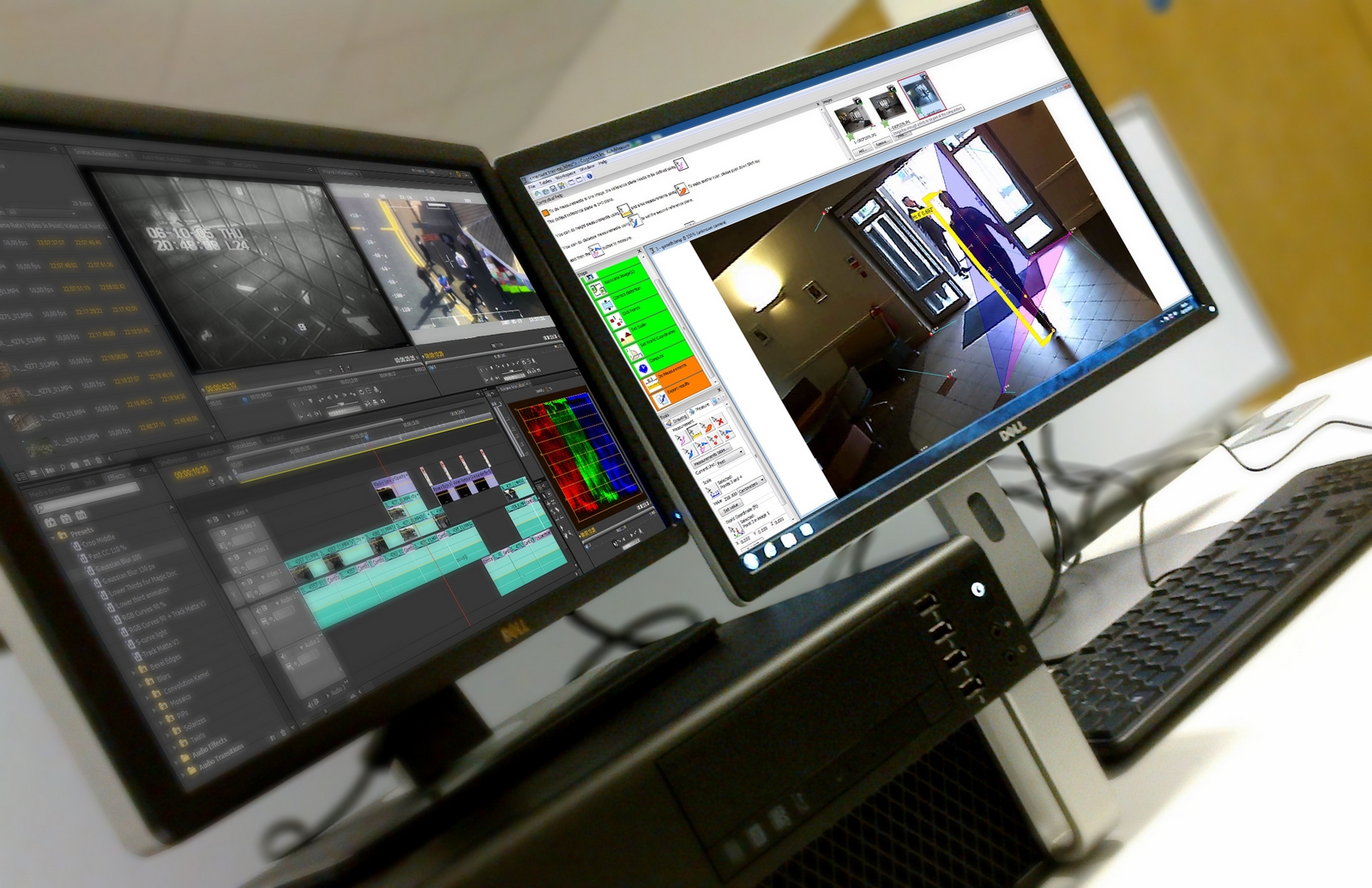
In today’s digital age, where data is continuously created, transferred, and stored, digital forensic investigation has become essential in solving crimes and uncovering cyber threats. Digital forensic investigation is a branch of forensic science focused on identifying, collecting, preserving, and analyzing digital data to support legal processes. This data, known as digital evidence, plays a critical role in investigations and is obtained through various forensic technologies. Understanding digital forensic investigation, its process, and the role of digital evidence and forensic technology is vital in today’s cybersecurity landscape.
What is Digital Forensic Investigation?
Digital forensic investigation involves examining digital devices like computers, smartphones, servers, and networks to extract valuable information relevant to an investigation. This field is instrumental in cybercrime cases, such as hacking, identity theft, and data breaches, as well as in more traditional criminal cases where digital evidence is present, like fraud or even murder cases where digital footprints may provide clues. Digital forensic investigation is also used in corporate settings to investigate intellectual property theft, employee misconduct, and regulatory compliance violations.
The process of digital forensic investigation includes the following key steps:
- Identification – Determining the type of evidence available and identifying the sources.
- Preservation – Ensuring the digital evidence remains unchanged and secure.
- Analysis – Examining the preserved evidence to uncover relevant information.
- Documentation – Recording findings and maintaining a clear chain of custody.
- Presentation – Presenting the findings in a court of law or to relevant authorities.
Each step must be carried out meticulously, as digital evidence can be easily tampered with, damaged, or altered, which could affect the outcome of the investigation.
Digital Evidence: The Core of Forensic Investigations
Digital evidence consists of information stored or transmitted in binary form that may be used in court. Examples include emails, social media messages, files on computers, log data, and metadata associated with various digital files. Forensic investigators often examine both the visible and hidden aspects of data, including deleted files, cached information, and even remnants in system memory.
However, digital evidence is unique because it is highly susceptible to corruption and alteration. Therefore, handling digital evidence requires strict protocols to ensure its integrity. Digital forensic investigators use specialized tools to ensure that evidence is preserved accurately and securely. Moreover, due to the evolving nature of digital devices and platforms, digital evidence can originate from numerous sources, from traditional devices like computers to IoT devices and cloud storage services.
Forensic Technology in Digital Investigations
Forensic technology refers to the tools and methods used to acquire, preserve, and analyze digital evidence. Some widely-used forensic technologies include:
- Disk Imaging Tools: These tools create an exact copy of a digital storage device. By working on a replica, investigators ensure the original data remains unaltered.
- Data Recovery Software: Used to retrieve deleted or corrupted files, data recovery software allows investigators to access information that may not be immediately visible.
- Network Forensics Tools: These tools analyze network traffic to detect unauthorized access, malware activity, and potential data exfiltration.
- Mobile Device Forensics: Given the widespread use of smartphones, specialized tools have been developed to extract and analyze data from these devices, including messages, call logs, and app data.
- Cloud Forensics: As cloud storage becomes more common, forensic technology has adapted to access and analyze data stored remotely.
In addition to these tools, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are beginning to play significant roles in automating data analysis, helping forensic teams to identify patterns and potential evidence faster and more accurately.
Challenges in Digital Forensic Investigation
While digital forensic investigation is highly effective, it faces several challenges. First, rapid technological advancements mean that new devices and software emerge continuously, requiring forensic investigators to stay updated on the latest tools and techniques. Additionally, encryption and privacy laws sometimes limit investigators’ ability to access data, particularly in cases involving mobile devices or encrypted communications.
Another challenge is data volume. The vast amount of data generated daily requires efficient tools and methods to sift through enormous datasets. Additionally, forensic investigators must be careful to follow strict protocols for preserving data integrity, as mishandling evidence could result in legal inadmissibility.
Conclusion
Digital forensic investigation is a critical component of modern crime-solving, cyber defense, and corporate security. By leveraging digital evidence and advanced forensic technology, investigators can uncover essential information to support legal cases and protect organizations. Despite the challenges posed by rapid technological evolution and data privacy concerns, digital forensic investigation remains an invaluable field that evolves alongside digital technology. Its role in the fight against cybercrime and digital threats highlights the importance of investing in forensic technology and developing expertise to ensure a safer digital future.




Leave a Reply